🎧 You can listen to this article instead of reading it
Choosing the right Tech Stack for your project is no longer a secondary decision. It has become a critical factor in the success of any modern web product.
With the rapid evolution of technologies, the emergence of new frameworks, and changing market demands, one key question stands out:
What is the best Tech Stack for a web project in 2026?

In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take you on a practical and realistic journey to explore the most popular web tech stacks, analyze their strengths and weaknesses, and identify the best use cases for each stack—without exaggeration or unrealistic promises.
This article is intended for:
- Beginner and intermediate developers
- Tech entrepreneurs and founders
- Teams planning to build long-term web products
What Is a Tech Stack and Why Does It Matter?#
A Tech Stack is the collection of technologies used to build a web application. It typically includes:
- Front-End: What users see and interact with
- Back-End: Application logic and data processing
- Database: Data storage layer
- Tools & Services: Hosting, APIs, and supporting tools
Choosing the right tech stack directly affects:
- Development speed
- Maintenance and scalability
- Project cost
- Hiring and team availability
💡 Important Note
There is no perfect tech stack for every project, but there is always a more suitable one based on goals, resources, and product nature.
Criteria for Choosing the Right Tech Stack in 2026#
Before diving into the stacks themselves, here are the key criteria used in this guide:
- Stability and maturity
- Community size and support
- Performance
- Learning curve
- Job market demand
- Integration with modern tools
- Long-term sustainability
The 8 Most Popular Web Tech Stacks#
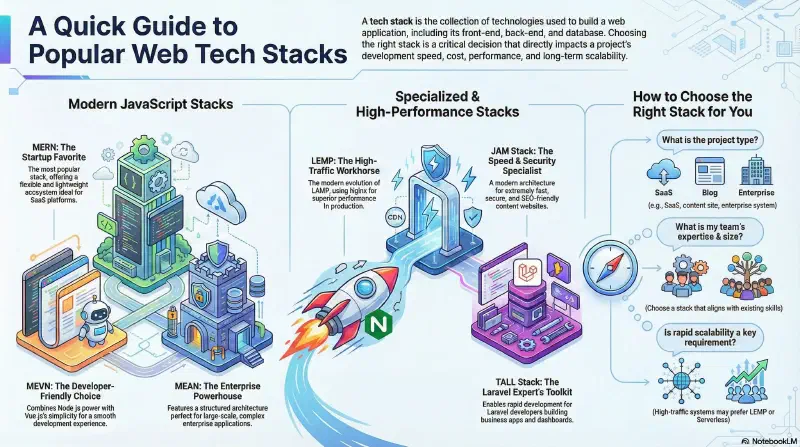
This article covers eight of the most widely used tech stacks in the web industry today, with a strong focus on stacks that are relevant now and expected to remain important in 2026.
1. MEAN Stack#
MEAN Stack Components#
- MongoDB – NoSQL database
- Express.js – Back-end framework
- Angular – Front-end framework
- Node.js – JavaScript runtime
Why MEAN Stack?#
MEAN Stack was one of the first stacks to introduce the concept of full-stack JavaScript, using the same language across all layers.
Pros#
- Clear and structured architecture
- Angular is powerful for large-scale applications
- Suitable for enterprise-level systems
- Strong backing from Google
Cons#
- Steep learning curve with Angular
- Overkill for small projects
- Requires solid architectural experience
When to Choose It?#
- Large and complex applications
- Enterprise systems
- Well-structured development teams
📝 Note
MEAN is still in use, but it is less popular than MERN for new projects.
2. MERN Stack#
MERN Stack Components#
- MongoDB
- Express.js
- React
- Node.js
Why MERN Stack?#
MERN is currently one of the most popular tech stacks in web development, especially among startups.
Pros#
- Flexible and lightweight React ecosystem
- Massive community and third-party libraries
- Excellent performance
- Ideal for SPA and SaaS products
Cons#
- Requires smart architectural decisions
- Tool overload can confuse beginners
- No strict default structure
When to Choose It?#
- Modern web applications
- SaaS platforms
- Dashboards
- Startup products
⭐ Reality Check
MERN remains one of the strongest choices in 2026 in terms of demand and job opportunities.
3. MEVN Stack#
MEVN Stack Components#
- MongoDB
- Express.js
- Vue.js
- Node.js
Why MEVN Stack?#
MEVN combines the power of Node.js with the simplicity of Vue.js, making it a favorite for developers seeking a smooth development experience.
Pros#
- Vue is easy to learn
- Clean and organized structure
- Excellent performance
- Suitable for mid-sized projects
Cons#
- Smaller job market than React
- Fewer learning resources
- Lower enterprise adoption
When to Choose It?#
- Medium-sized projects
- Small teams
- Admin panels
💬 Quote
“Vue makes development enjoyable without unnecessary complexity.”
4. JAM Stack#
What Is JAM Stack?#
JAM is not a traditional stack but a modern web architecture based on:
- JavaScript
- APIs
- Markup
Why JAM Stack?#
JAM Stack emerged to address the need for:
- High performance
- Better security
- Lower infrastructure costs
Pros#
- Extremely fast load times
- Strong security model
- SEO-friendly
- Ideal for static content
Cons#
- Not suitable for complex applications
- Heavy reliance on third-party services
- State management can be tricky
When to Choose It?#
- Content-driven websites
- Blogs
- Landing pages
- Corporate websites
⚠️ Important Warning
JAM Stack is not a replacement for all applications—it excels in specific use cases only.
5. TALL Stack#
TALL Stack Components#
- Tailwind CSS
- Alpine.js
- Laravel
- Livewire
Why TALL Stack?#
TALL Stack is a smart choice for Laravel developers who want a modern experience without React or Vue.
Pros#
- Rapid development workflow
- Seamless Laravel integration
- Ideal for business applications
- Clean and maintainable code
Cons#
- Tightly coupled with Laravel
- Smaller community
- Limited global adoption
When to Choose It?#
- Admin dashboards
- Laravel-based projects
- Business applications
🛠️ Practical Note
TALL Stack is perfect if you’re a backend developer who wants a simple yet effective frontend.
6. LAMP Stack (Modern Version)#
LAMP Stack Components#
- Linux
- Apache
- MySQL
- PHP
Why Is LAMP Still Relevant?#
Despite its age, LAMP has evolved significantly, especially with:
- PHP 8+
- Laravel
- Performance optimizations
Pros#
- Highly stable
- Low hosting costs
- Huge developer community
- Suitable for traditional websites
Cons#
- Less modern compared to newer stacks
- Not ideal for SPAs
- Weaker frontend experience
When to Choose It?#
- Company websites
- Traditional systems
- Budget-limited projects
7. LEMP Stack#
LEMP Stack Components#
- Linux – Operating system
- Nginx – Web server
- MySQL / MariaDB – Database
- PHP – Programming language (often with Laravel or Symfony)
Why LEMP Stack?#
LEMP is the natural evolution of LAMP, replacing Apache with Nginx to achieve better performance under high traffic.
In recent years, LEMP has become a preferred choice for systems that require:
- Fast response times
- Lower resource consumption
- Long-term stability
Pros#
- Better performance than LAMP
- Nginx handles high traffic efficiently
- Excellent for modern Laravel applications
- Strong production stability
Cons#
- Nginx configuration is more complex
- Requires better server management skills
- Less beginner-friendly
When to Choose LEMP Stack?#
- High-traffic web applications
- Long-term business systems
- Laravel projects in production
- Performance-critical websites
📝 Important Note
If you use Laravel and plan to deploy on a real server, LEMP is often a more practical choice than LAMP.
LAMP vs LEMP: A Detailed Comparison#
Although LAMP and LEMP share a similar foundation, the core difference between them has a major impact on performance and scalability.
💡 Quick Insight
The real difference lies not in PHP or MySQL, but in how the web server handles requests.
Key Differences#
| Aspect | LAMP Stack | LEMP Stack |
|---|---|---|
| Web Server | Apache | Nginx |
| Architecture | Process-based | Event-driven |
| Resource Usage | Higher | Lower and more efficient |
| High Traffic Handling | Good | Excellent |
| Setup Ease | Beginner-friendly | Requires experience |
| Overall Performance | Stable | Faster in most cases |
Performance and Scalability#
LAMP
- Apache processes requests sequentially
- Suitable for medium-traffic websites
- Stable but less efficient at scale
LEMP
- Designed to handle thousands of concurrent requests
- Better for high-traffic systems
- Lower memory usage
Security and Stability#
- Both stacks are secure when properly configured
- Nginx has a smaller attack surface
- Apache relies more on extensions
🔐 Security Reminder
Security depends more on proper configuration and updates than on the stack itself.
8. Serverless Stack#
What Is a Serverless Stack?#
A Serverless Stack typically includes:
- Front-end framework
- Cloud functions
- Managed databases
Examples:
- AWS Lambda
- Firebase
- Supabase
Pros#
- No server management
- High scalability
- Pay-as-you-go pricing
Cons#
- Vendor lock-in
- More difficult debugging
- Unpredictable costs
When to Choose It?#
- MVPs
- Rapid development projects
- Applications with variable traffic
Quick Comparison of Popular Tech Stacks#
| Stack | Learning Curve | Performance | Job Demand | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEAN | Medium | High | Medium | Enterprise |
| MERN | Good | Very High | High | SaaS |
| MEVN | Easy | High | Medium | Mid-sized projects |
| JAM | Easy | Excellent | Good | Content |
| TALL | Medium | Very Good | Medium | Laravel |
| LAMP | Easy | Good | Good | Traditional websites |
| LEMP | Medium | Very High | Good | High-performance systems |
| Serverless | Medium | High | Growing | MVPs |
How to Choose the Best Tech Stack for You?#
Ask yourself:
- What type of project am I building?
- How large is the team?
- What is the budget?
- Is this a long-term product?
- Do I need rapid scalability?
🎯 Practical Conclusion
Don’t choose a tech stack because it’s trendy—choose it because it serves your project effectively.
Tech Stack Trends in 2026#
- Continued dominance of MERN Stack
- Increased adoption of Serverless architectures
- Growing use of JAM Stack for content-driven sites
- Laravel maintaining a strong position
- Strong focus on flexibility and development speed
Choosing from the most popular web tech stacks is not about picking the most powerful option technically, but the most practical one for your real-world needs.
This guide is designed to be a reliable reference you can return to anytime—whether you’re starting your first project or planning a large-scale product in 2026.
✨ Final Advice
Technology is a tool, not the goal. The real goal is building a successful product that serves users effectively.